Your Guide to 2023’s
Top Anti-Inflammation Supplements
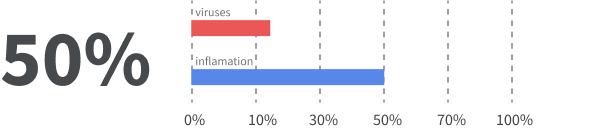
With mounting evidence uncovering the severity of chronic inflammation, it makes sense that more medical experts and patients are exploring more ways to prevent, manage, and, even, reverse chronic inflammation before it’s too late.
What is inflammation?
Inflammation is one of our most vital functions. Without inflammation we could not properly fight off infections and heal from injuries. But, like every process in the body, balance is essential. When inflammation persists after an initial threat has passed, the very defense mechanism that was working for the body turns against it, resulting in chronic inflammation and inflammation-induced conditions.
The effects of chronic inflammation can impact almost every system in the body—digestive, neurological, musculoskeletal, hormonal. But despite its far reach, chronic inflammation is surprisingly tricky to spot in advance.
Chronic conditions are increasingly common, and research indicates that nearly 3 in 5 Americans live with at least one chronic condition—a number that is expected to rise incrementally over the next 30 years.2 To combat the prevalence of chronic inflammation, more people are searching for daily preventative measures.
Today’s wellness market is saturated with products targeting inflammation. To help you navigate the pharmacy aisles more proficiently, we’ve created a guide to understanding inflammation and which ingredients most efficiently manage it.
What Causes Inflammation?

Diet
Diet is one of the biggest instigators of chronic inflammation and can spark the onset of chronic conditions like obesity, type 2 diabetes, joint pain, and heart disease. According to studies, dietary habits that are high in refined starches, sugars, saturated and trans-fatty acids can trigger the body to produce more pro-inflammatory cytokines (small proteins that influence immune system responses).3 Further, diets filled with pro-inflammatory ingredients are generally lower in vital anti-inflammatory ingredients. Focusing eating patterns around omega-3 fatty acids, whole grains, and antioxidant-rich fruits and vegetables have been shown to reduce inflammation and chronic disease.

Stress and depression
Managing stress is not just vital for our emotional wellbeing, but also for our long-term physical health. Research has long suggested an almost-cyclical relationship between stress and depression, and chronic inflammation. Experiencing ongoing stress can cause endocrine and immune system dysfunction, subsequently triggering low-grade inflammation and activating further development of depression.4 Our bodies are not built to withstand unrelenting stress. But unfortunately, modern lifestyle precipitates greater stress.

Exposure to environmental toxins
Our external environments play a huge role in shaping our internal health. Research reveals that the presence of chemicals in the air, or water or food supply spur inflammation.5 When our bodies sense external threats, including the presence of inorganic chemicals, it increases the production of proinflammatory cytokines to fend off the threat. And constant exposure activates a steady uptick of cytokines, naturally leading to chronic inflammation. Certain chemicals known as endocrine disruptors (including chemicals found in plastics and pesticides) have also been shown to alter the microbiome in our gut, leading to further stress and inflammation.6
Untreated infection
When the body senses the threat of a potential infection, it releases an inflammatory counter-attack to protect our tissues and organs. This response is only meant to be temporary, but sometimes the inflammatory response lingers for too long, prompting white blood cells to turn on the body and begin attacking healthy cells and tissue.
How to manage inflammation with the right ingredients
Supplementing your daily diet with ingredients that have been proven to decrease inflammation, can not only increase your quality of life in the short-term by improving mobility and reducing pain, but can also strengthen your defenses against chronic diseases like arthritis, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and Alzheimer’s.
Top Anti-Inflammatory Ingredients

Tetrohydrocurcumin counters inflammation by eliminating reactive oxygen species and suppressing pro-inflammatory proteins that bind genes to DNA.7,8
Tetrohydrocurcumin is noted for its protection against pro-inflammatory diseases like cardiovascular disease, autoimmune diseases, depression, and more.

A patented and naturally-occurring, energy-boosting antioxidant.
Mitoprime is a more bioavailable formulation, and protects DNA from oxidative damage, prevents cell death and mitochondrial damage, and reduces age-related cognitive decline.9,10

Dihydroberberine is a naturally-occurring derivative of berberine.
Which is known as a molecule found in plants that activates an enzyme known to improve insulin sensitivity, enhance lipid oxidation (the process in which fat is utilized for energy), inhibit adipocyte (fat cell) growth and improve cardiovascular health . Dihydroberberine is more naturally absorbed than berberine. 11,12

A powerful anti-inflammatory, plant-derived chemical that blocks proinflammatory molecules.
trans-Resveratrol restores cognitive impairment and extends longevity by supporting anti-aging enzymes.13,14

With its potent anti-inflammatory properties, ginger root can reduce symptoms of arthritis.
By suppressing pro-inflammatory molecules, ginger root protects the body from the onset of inflammation-induced conditions like diabetes, arthritis, Crohn’s disease, and more.15,16

Vitamin B12 offers a range of supplementary benefits, including enhancing energy and reducing pain.
BVitamin B12 supplementation can significantly reduce pain and has been shown to reduce local inflammation following tissue injuries.17,18
Beware of These Popular Anti-Inflammation Supplements
When will you notice results?
It’s common to begin to feel the positive effects from effective anti-inflammatory supplements around the 60 and 90 day marks.
How to Choose the Best Supplement
Bioavailability refers to how easy it is for your body to absorb ingredients.
For example, tetrohydrocurcumin is a more bio-available formulation of curcumin. Supplementing with ingredients that are easier to absorb and metabolize means that the benefits—like inflammation reduction and cellular protection—are more potent.
Formulation under the guidance of doctors fosters efficacy.
From working with patients everyday, Doctors have a profound understanding of what causes inflammation—and how to fight it.
Ingredients vetted by multiple studies promote efficacy and safety.
Not every supplement is created equal. Looking for ingredients that have been verified by clinical research is the most assured way to distinguish worthy supplements.
Top 3 Anti-Inflammation Supplements of 2023
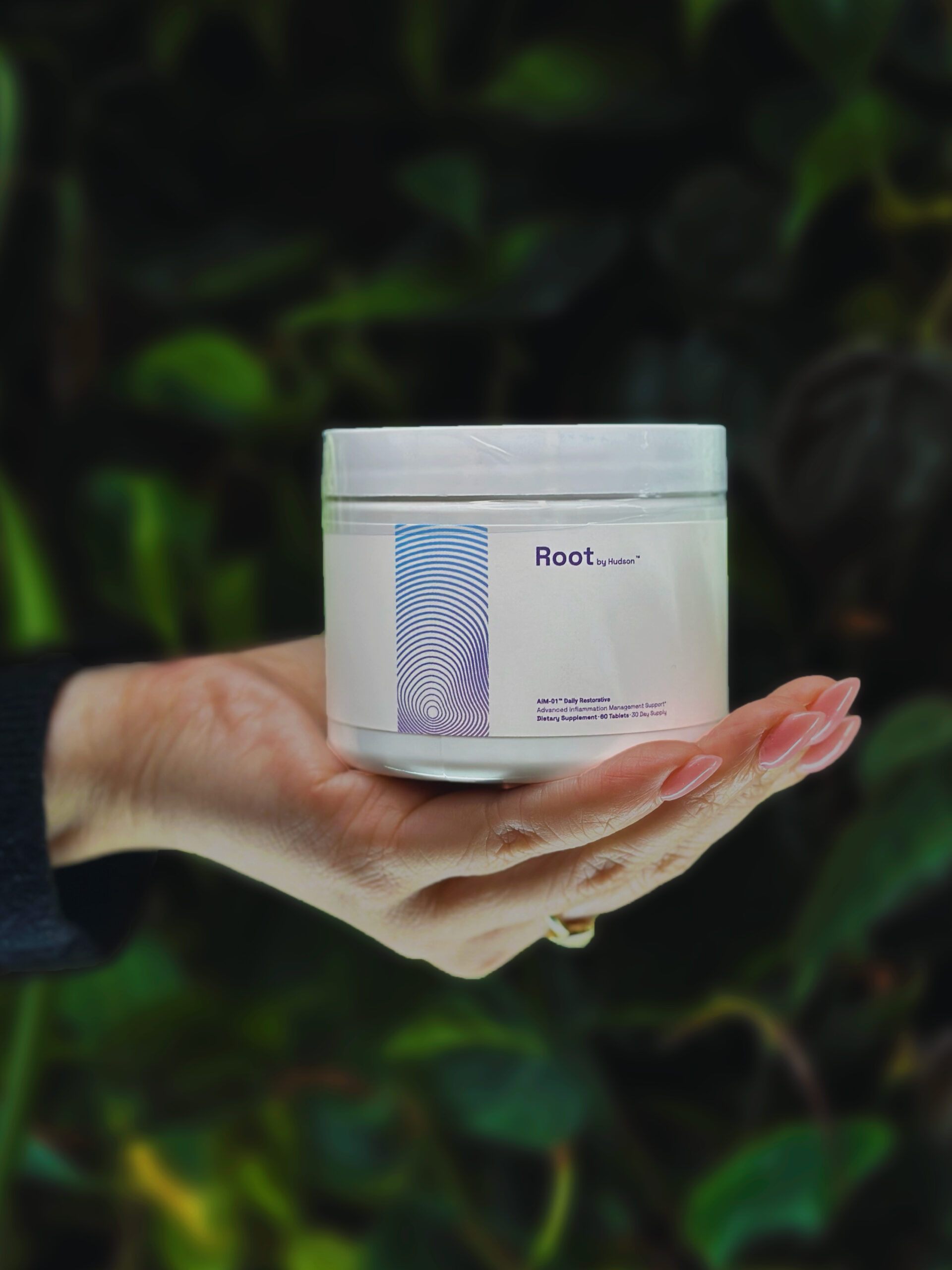
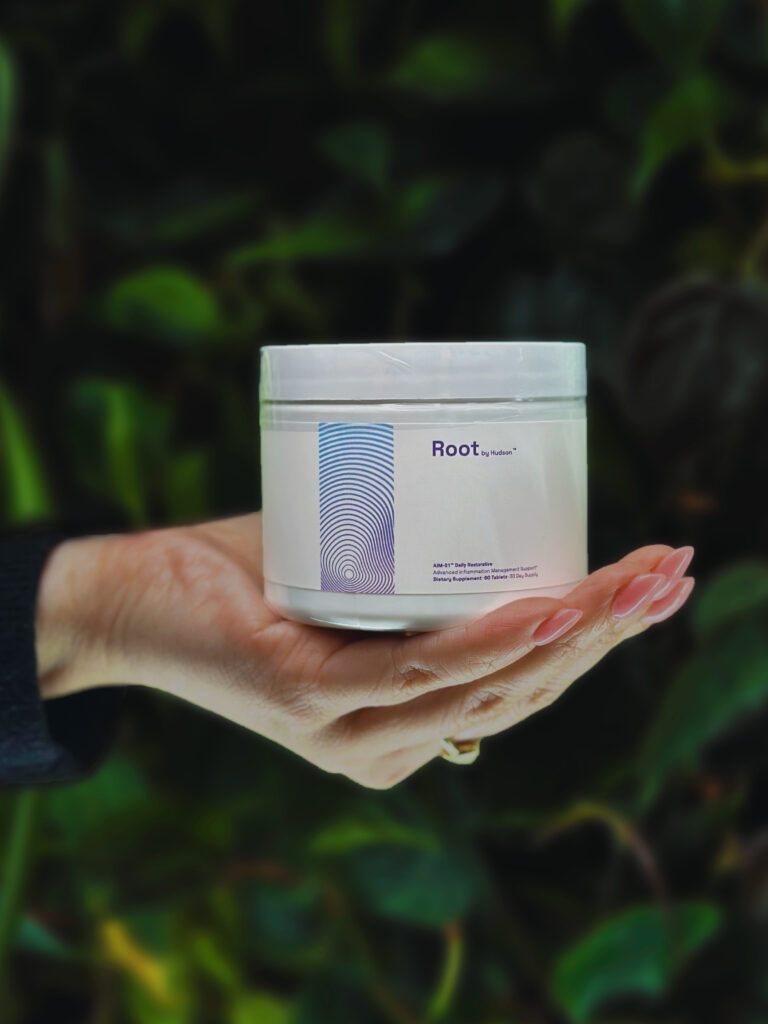
1. AIM-01:
Advanced Inflammation Management

A+
Overall Grade
AIM-01 is currently available for purchase online and at Hudson Health’s TriBeCa and West Village offices in New York City.

1. AIM-01:
Advanced Inflammation Management

A+
Overall Grade
AIM-01 is currently available for purchase online and at Hudson Health’s TriBeCa and West Village offices in New York City.
Pros
Cons
2.Ibuprofen (generic)
As a widely available OTC drug, Ibuprofen is one of the most common supplements people reach for to diminish pain and fevers. Too much dependence on Ibuprofen may result in ulcers, sub-optimal kidney function, and GI issues.
Pros
Cons
3. Curcumin
Curcumin is an active component of the turmeric spice. It comes from the root Curcuma longa, and has long been a staple of Ayurvedic medicine. It is often used to treat skin and digestive issues and is noted for its anti-inflammatory benefits.
Pros
Cons
- Furman, D., Campisi, J., Verdin, E. et al. Chronic inflammation in the etiology of disease across the life span. Nat Med 25, 1822–1832 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-019-0675-0
- Pahwa R, Goyal A, Jialal I. Chronic Inflammation. [Updated 2022 Jun 19]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK493173/
- Dario Giugliano, Antonio Ceriello, Katherine Esposito,
- The Effects of Diet on Inflammation: Emphasis on the Metabolic Syndrome, Journal of the American College of Cardiology, Volume 48, Issue 4, 2006, Pages 677-685, ISSN 0735-1097, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2006.03.052.
- Maydych V. The Interplay Between Stress, Inflammation, and Emotional Attention: Relevance for Depression. Front Neurosci. 2019 Apr 24;13:384. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00384. PMID: 31068783; PMCID: PMC6491771.
- Heindel JJ, Blumberg B, Cave M, Machtinger R, Mantovani A, Mendez MA, Nadal A, Palanza P, Panzica G, Sargis R, Vandenberg LN, Vom Saal F. Metabolism disrupting chemicals and metabolic disorders. Reprod Toxicol. 2017 Mar;68:3-33. doi: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2016.10.001. Epub 2016 Oct 17. PMID: 27760374; PMCID: PMC5365353.
- Gálvez-Ontiveros Y, Páez S, Monteagudo C, Rivas A. Endocrine Disruptors in Food: Impact on Gut Microbiota and Metabolic Diseases. Nutrients. 2020 Apr 21;12(4):1158. doi: 10.3390/nu12041158. PMID: 32326280; PMCID: PMC7231259.
- Singh S, Aggarwal BB. Activation of transcription factor NF-kappa B is suppressed by curcumin (diferuloylmethane) [corrected] [published correction appears in J Biol Chem 1995 Dec 15;270(50):30235]. J Biol Chem. 1995;270(42):24995-25000. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.42.24995
- Nakamura Y, Ohto Y, Murakami A, Osawa T, Ohigashi H. Inhibitory effects of curcumin and tetrahydrocurcuminoids on the tumor promoter-induced reactive oxygen species generation in leukocytes in vitro and in vivo. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1998;89(4):361-370. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.1998.tb00572.x
- “What Are Common Symptoms of Autoimmune Disease?” Johns Hopkins Medicine, 22 July 2022, https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/wellness-and-prevention/what-are-common-symptoms-of-autoimmune-disease#:~:text=Autoimmune%20Disease%20Basics,wide%20range%20of%20body%20parts”
- Edwin McDonald, MD. “Foods That Cause Inflammation & How to Reduce Inflammation.” Foods That Cause Inflammation & How to Reduce Inflammation – UChicago Medicine, UChicago Medicine, 4 Sept. 2020, https://www.uchicagomedicine.org/forefront/gastrointestinal-articles/what-foods-cause-or-reduce-inflammation#:~:text=All%20processed%20foods%20can%20cause,that%20leads%20to%20chronic%20inflammation”>https://www.uchicagomedicine.org/forefront/gastrointestinal-articles/what-foods-cause-or-reduce-inflammation#:~:text=All%20processed%20foods%20can%20cause,that%20leads%20to%20chronic%20inflammation
- 11.Dai B, Ma Y, Wang W, et al. Dihydroberberine exhibits synergistic effects with sunitinib on NSCLC NCI-H460 cells by repressing MAP kinase pathways and inflammatory mediators. J Cell Mol Med. 2017;21(10):2573-2585. doi:10.1111/jcmm.13178
- 12.Xu L, Lin G, Yu Q, et al. Anti-Hyperuricemic and Nephroprotective Effects of Dihydroberberine in Potassium Oxonate- and Hypoxanthine-Induced Hyperuricemic Mice. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:645879. Published 2021 Apr 20. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.645879
- Li J, Zhang CX, Liu YM, Chen KL, Chen G. A comparative study of anti-aging properties and mechanism: resveratrol and caloric restriction. Oncotarget. 2017;8(39):65717-65729. Published 2017 Aug 9. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.20084
- Salehi B, Mishra AP, Nigam M, et al. Resveratrol: A Double-Edged Sword in Health Benefits. Biomedicines. 2018;6(3):91. Published 2018 Sep 9. doi:10.3390/biomedicines6030091
- Aggarwal BB, Shishodia S. Molecular targets of dietary agents for prevention and therapy of cancer. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006;71(10):1397-1421. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2006.02.009
- Habib SH, Makpol S, Abdul Hamid NA, Das S, Ngah WZ, Yusof YA. Ginger extract (Zingiber officinale) has anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory effects on ethionine-induced hepatoma rats. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2008;63(6):807-813.
- Hosseinzadeh H, Moallem SA, Moshiri M, Sarnavazi MS, Etemad L. Anti-nociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects of cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12) against acute and chronic pain and inflammation in mice. Arzneimittelforschung. 2012;62(7):324-329. doi:10.1055/s-0032-1311635
- Ehmedah A, Nedeljkovic P, Dacic S, et al. Vitamin B Complex Treatment Attenuates Local Inflammation after Peripheral Nerve Injury. Molecules. 2019;24(24):4615.
- Moon JM, Ratliff KM, Hagele AM, Stecker RA, Mumford PW, Kerksick CM. Absorption Kinetics of Berberine and Dihydroberberine and Their Impact on Glycemia: A Randomized, Controlled, Crossover Pilot Trial. Nutrients. 2021 Dec 28;14(1):124. doi: 10.3390/nu14010124. PMID: 35010998; PMCID: PMC8746601.

